PNPO
Gene product: Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase.
Protein function: It plays a key role in the synthesis of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) from pyridoxine phosphate and pyridoxamine phosphate. Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase deficiency can lead to severe PLP deficiency. PLP can participate in the synthesis of GABA as a coenzyme of glutamate decarboxylase.
Phenotype: Pyridox(am)ine-5-phosphate Oxidase deficiency (AR) (some may manifest as Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome)[1-2]。
Mutation database: ClinVar.
Clinical and basic research: PubMed (PMID: 24645144 (Brain. 2014); PMID: 36980111 (Children (Basel). 2023)).
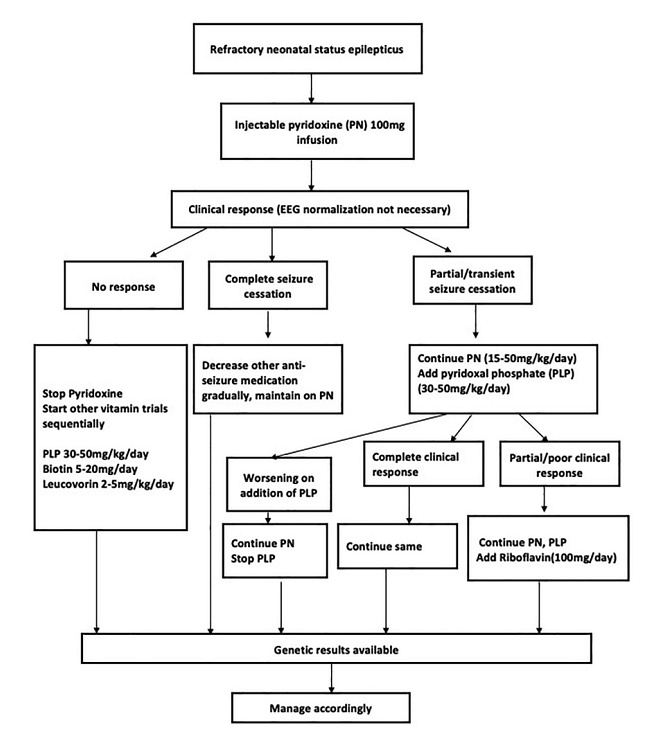
Medication reminder: Lifelong supplementation with pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, the active form of pyridoxine) or pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is required. For some children, supplementation with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) alone is often ineffective or only partially effective [2-3]. For the treatment of refractory neonatal status epilepticus (suspected vitamin B6-responsive epilepsy), please refer to the flow chart 1 [4].
Flow chart 1
References:
- Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Apr 15;14(8):1077-86.
- Brain. 2014 May;137(Pt 5):1350-60.
- Children (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;10(3):553.
- Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2021 Apr 3:16:100443.

 English
English  简体中文
简体中文 