MAP2K1
Gene product: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1.
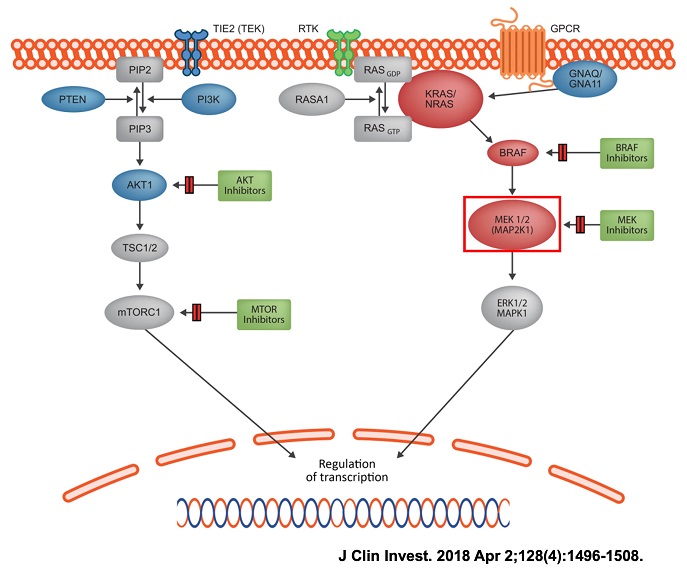
Protein function: A dual-specific protein kinase that is a key component of the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway (Figure 1) and plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, migration and metabolism[1-2]. Other literature reports MAP2K1 mutations also lead to overactivation of the mTOR signaling pathway and may be related to focal cortical dysplasia [7].
Phenotype: Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 3 (AD) (some may have developmental delay and seizures, and some may present with Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome) [3-6].
Mutation database: ClinVar.
Clinical research: PubMed (PMID: 37827855 (Am J Med Genet A. 2024))
Medication reminder: The choice of medication is mainly based on different Epilepsy Syndromes. Some of them may present as refractory epileptic seizures. Literature reports that some children have a good response to oxcarbazepine [5]. There is no relevant literature report on whether other relatively targeted treatments such as MEK inhibitors and mTOR inhibitors have a certain effect on epileptic seizures caused by this gene mutation. In addition, if imaging clearly indicates focal cortical dysplasia and the EEG also indicates it, surgery may also be an option for drug-resistant epilepsy caused by this gene mutation (there is no relevant literature report yet, personal opinion, for reference only).
Figure 1
References:
- The RASopathy Family: Consequences of Germline Activation of the RAS/MAPK Pathway. Endocr Rev. 2018 Oct 1;39(5):676-700.
- Mosaic RAS/MAPK variants cause sporadic vascular malformations which respond to targeted therapy. J Clin Invest. 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1496-1508.
- Mutation and phenotypic spectrum in patients with cardio-facio-cutaneous and Costello syndrome. Clin Genet. 2008 Jan;73(1):62-70.
- Long-term clinical course of adult-onset refractory epilepsy in cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome with a pathogenic MAP2K1 variant: a case report. Front Genet. 2024 Jul 17:15:1410979.
- Epilepsy in cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome: Clinical burden and response to anti-seizure medication. Am J Med Genet A. 2024 Feb;194(2):301-310.
- Infantile epileptic spasms syndrome in children with cardiofaciocutanous syndrome: Clinical presentation and associations with genotype. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022 Dec;190(4):501-509.
- An integrated genetic analysis of epileptogenic brain malformed lesions. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Mar 2;11(1):33.

 English
English  简体中文
简体中文 