RELN
基因产物:络丝蛋白(Reelin)。
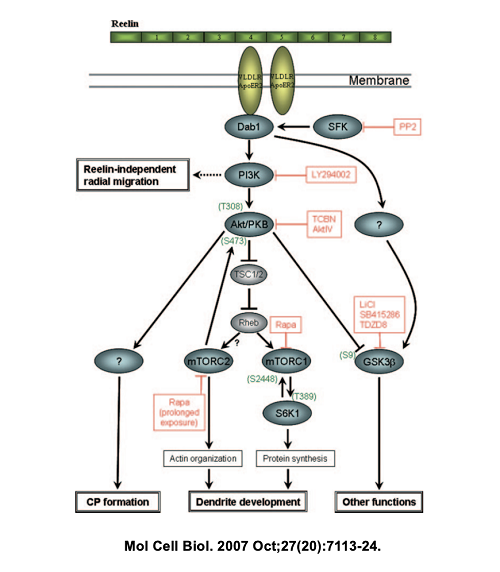
蛋白功能:属于细胞外基质丝氨酸蛋白酶,调节神经元微管功能和神经元迁移,另参与mTOR通路相关的调控(示意图1)[3]。
相关疾病:无脑回畸形(AR)[1];伴有听觉特点的常染色体显性遗传癫痫(家族性颞叶癫痫外侧型)(AD)[2]。
突变数据库:ClinVar数据库。
相关临床研究:PubMed数据库(PMID: 28142128 (Epilepsy Behav. 2017))
用药提醒:对于该基因变异所致的伴有听觉特点的常染色体显性遗传癫痫(家族性颞叶癫痫外侧型),患儿多数对抗癫痫发作药物反应敏感,预后较好,往往单一用药就能控制(传统上针对该综合症钠通道阻滞类的抗癫痫发作药物使用频率会更高点且具有明确疗效,可优先考虑,目前尚未见到明确某个药物优于另一个药物的报道),部分患儿停药后可能会复发[4-5]。
讨论版块:点击进入RELN基因突变讨论版块。
示意图1
参考文献
- Hong, S.E., et al., Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations.Nat Genet, 2000. 26(1): p. 93-6.
- Dazzo, E., et al., Heterozygous reelin mutations cause autosomal-dominant lateral temporal epilepsy.Am J Hum Genet, 2015. 96(6): p. 992-1000.
- Reelin signals through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt to control cortical development and through mTor to regulate dendritic growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(20):7113-24.
- The clinical phenotype of autosomal dominant lateral temporal lobe epilepsy related to reelin mutations. Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Mar:68:103-107.
- Autosomal Dominant Epilepsy with Auditory Features. GeneReviews, 2024.

 English
English  简体中文
简体中文 